为什么需要 key
abstract class StatelessWidget extends Widget {
/// Initializes [key] for subclasses.
const StatelessWidget({super.key});
}
@immutable
abstract class Widget extends DiagnosticableTree {
/// Initializes [key] for subclasses.
const Widget({this.key});
final Key? key;
}
在 Flutter 里,任何 widget 都可以有一个 key,它是 Flutter 框架 高效管理 widget 树 的核心机制之一。
在 Flutter 里,界面是通过不断 重新构建 widget 树 实现刷新的。但是 widget 是 immutable(不可变) 的,一旦变化就会创建新的对象。
因此,框架需要一种方法判断:新旧 widget 是否对应。
在大部分情况下,其实不需要判断新旧 widget 是否对应,因为大部分是静态 UI,不需要 key。
只有在widget的动态 UI时,这个时候必须用 key
- 列表/ListView/GridView:items 增删/重排时,如果没 key,Flutter 只按位置匹配,内容和输入状态可能错乱。
- 动画/切换时:比如
PageView或TabBarView,不同页面的子 widget 类型一样,但其实身份不同,需要 key 区分。 - 复用相同类型 widget 但身份不同:例如两个
TextField都是TextField类型,但一个是“用户名”,另一个是“密码”,如果它们在树里的相对顺序发生变化,就必须用 key 区分,不然输入内容会串。
key 的作用 :唯一标识一个 widget
flutter 的匹配复用规则
匹配和复用的真正含义
Flutter 的三层概念
理解复用,先要知道 Flutter 的三层概念:
- Widget:
- 轻量级、不可变(immutable),只是一个配置。
- 每次
build()时,都会重新创建新的 widget 对象。
- Element:
- Widget 在树中的“位置”和“桥梁”,管理生命周期。
- 持有 widget + state。
- RenderObject:负责真正的绘制和布局,开销最大。
真正含义
当 Flutter 重新 build 时:
- Widget:一定是新建的(不可变,没法复用)。
- Element & State:如果能匹配(位置相同 + 类型相同 + key 相同/都没有 key),就会复用旧的 Element 和 State,只替换其中的 widget 引用。
- RenderObject:如果 widget 类型相同,通常也会复用原来的 RenderObject。
这里的“复用”指的是:复用 Element/State/RenderObject,而不是复用旧的 widget。
下面会结合案例进行说明。
没有 key 时的匹配规则
没有 key 时:
- 匹配规则:按位置 + 类型。
- 如果新旧树 index 相同 且 widget 类型相同 → 复用旧的
Element/State/RenderObject。 - 问题:一旦顺序变化,就会错位复用,导致 UI/状态混乱。
案例
import 'package:flutter/material.dart';
void main() {
runApp(const MaterialApp(home: MyListDemo()));
}
class MyListDemo extends StatefulWidget {
const MyListDemo({super.key});
@override
State<MyListDemo> createState() => _MyListDemoState();
}
class _MyListDemoState extends State<MyListDemo> {
List<String> items = ["A", "B", "C"];
void swapItems() {
setState(() {
items.insert(0, items.removeAt(2)); // 把最后一个移动到最前面
});
}
@override
Widget build(BuildContext context) {
return Scaffold(
appBar: AppBar(title: const Text("List Demo - No Key")),
body: ListView(
children: items.map((e) {
return ListTile(
title: Text(e),
// ❌ 没有 key
);
}).toList(),
),
floatingActionButton: FloatingActionButton(
onPressed: swapItems,
child: const Icon(Icons.swap_horiz),
),
);
}
}
日志如下:
Restarted application in 3,540ms.
I/flutter (17988): Items after swap: [C, A, B]
I/flutter (17988): Items after swap: [B, C, A]
I/flutter (17988): Items after swap: [A, B, C]

flutter内部如何匹配和复用
初始状态(items = ["A", "B", "C"])
Widget Tree Element Tree (持有State/RenderObject)
---------------------------------------------------------------
ListTile(Text("A")) ──▶ Element[0] ──▶ RenderObject("A")
ListTile(Text("B")) ──▶ Element[1] ──▶ RenderObject("B")
ListTile(Text("C")) ──▶ Element[2] ──▶ RenderObject("C")
调用 swapItems() 后(items = ["C", "A", "B"])
新建的 Widget Tree:
ListTile(Text("C")) (index 0) ListTile(Text("A")) (index 1) ListTile(Text("B")) (index 2)Flutter 匹配逻辑(没 key):
index 0:旧的Element[0]复用,但它之前绑定的是"A"→ ❌ 错乱index 1:旧的Element[1]复用,但它之前绑定的是"B"→ ❌ 错乱index 2:旧的Element[2]复用,但它之前绑定的是"C"→ ❌ 错乱
Widget Tree (新) Element Tree (旧的被复用,导致错位) --------------------------------------------------------------- ListTile(Text("C")) ──▶ Element[0] ──▶ RenderObject("A") (错) ListTile(Text("A")) ──▶ Element[1] ──▶ RenderObject("B") (错) ListTile(Text("B")) ──▶ Element[2] ──▶ RenderObject("C") (错)结果:
- 无状态 widget(StatelessWidget) → 只是显示内容和预期不一致(轻微问题)。
- 如上面案例:UI 没有正确变成
C, A, B,内容错乱。
- 如上面案例:UI 没有正确变成
- 有状态 widget (StatefulWidget)→
State被错位复用,数据/交互直接乱掉(严重问题)。- 典型 bug:输入框的内容“跑到”别的行;选中的复选框错位。
- 无状态 widget(StatelessWidget) → 只是显示内容和预期不一致(轻微问题)。
有 key 时的匹配规则
有 key 时:
- 匹配规则:按 key + 类型。
- 如果新旧树 key 相同 且 widget 类型相同 → 复用旧的
Element/State/RenderObject。 - 即使顺序变化,也能正确找到对应 widget,不会错位。
案例
body: ListView(
children: items.map((e) {
return ListTile(
key: ValueKey(e), // ✅ 每个 item 有唯一 key
title: Text(e),
);
}).toList(),
),
日志如下:
I/flutter (22299): Items after swap: [C, A, B]
I/flutter (22299): Items after swap: [B, C, A]

flutter内部如何匹配和复用
如果给每个 item 一个 key: ValueKey(e),那么匹配逻辑变成 按 key 匹配:
ListTile(Text("C"), key:"C") → 旧的 Element("C") → RenderObject("C")
ListTile(Text("A"), key:"A") → 旧的 Element("A") → RenderObject("A")
ListTile(Text("B"), key:"B") → 旧的 Element("B") → RenderObject("B")
这样匹配就正确,不会错位。UI 正确更新为:C, A, B ✅
Key 的几种类型
ValueKey<T>
直接用一个值作为标识。
常用于唯一 ID,比如列表项:
ListView(
children: items.map((e) => Text(e.name, key: ValueKey(e.id))).toList(),
)
ObjectKey
用对象本身的 == 和 hashCode 来标识。
如果两个对象逻辑上相等(比如 id 相同),会被认为是同一个 widget。
import 'package:flutter/material.dart';
void main() => runApp(const MaterialApp(home: ObjectKeyDemo()));
class Item {
final int id;
final String name;
Item(this.id, this.name);
@override
bool operator ==(Object other) =>
identical(this, other) || (other is Item && other.id == id);
@override
int get hashCode => id.hashCode;
}
class ObjectKeyDemo extends StatefulWidget {
const ObjectKeyDemo({super.key});
@override
State<ObjectKeyDemo> createState() => _ObjectKeyDemoState();
}
class _ObjectKeyDemoState extends State<ObjectKeyDemo> {
List<Item> items = [Item(1, "A"), Item(2, "B")];
void swap() {
setState(() {
items.insert(0, items.removeAt(1)); // 交换顺序
});
}
@override
Widget build(BuildContext context) {
return Scaffold(
appBar: AppBar(title: const Text("ObjectKey Demo")),
body: ListView(
children: items.map((item) {
return ListTile(
key: ObjectKey(item), // ✅ 使用对象作为 key
title: Text(item.name),
trailing: SizedBox(
// ✅ 给 TextField 约束宽度
width: 150,
child: TextField(
decoration: const InputDecoration(
border: OutlineInputBorder(),
hintText: "输入点内容",
),
),
),
);
}).toList(),
),
floatingActionButton: FloatingActionButton(
onPressed: swap,
child: const Icon(Icons.swap_horiz),
),
);
}
}
运行后,在输入框里输入点内容,然后点交换按钮:如果用 ObjectKey,状态不会错乱(输入框里的内容还在对应的 item 上)。
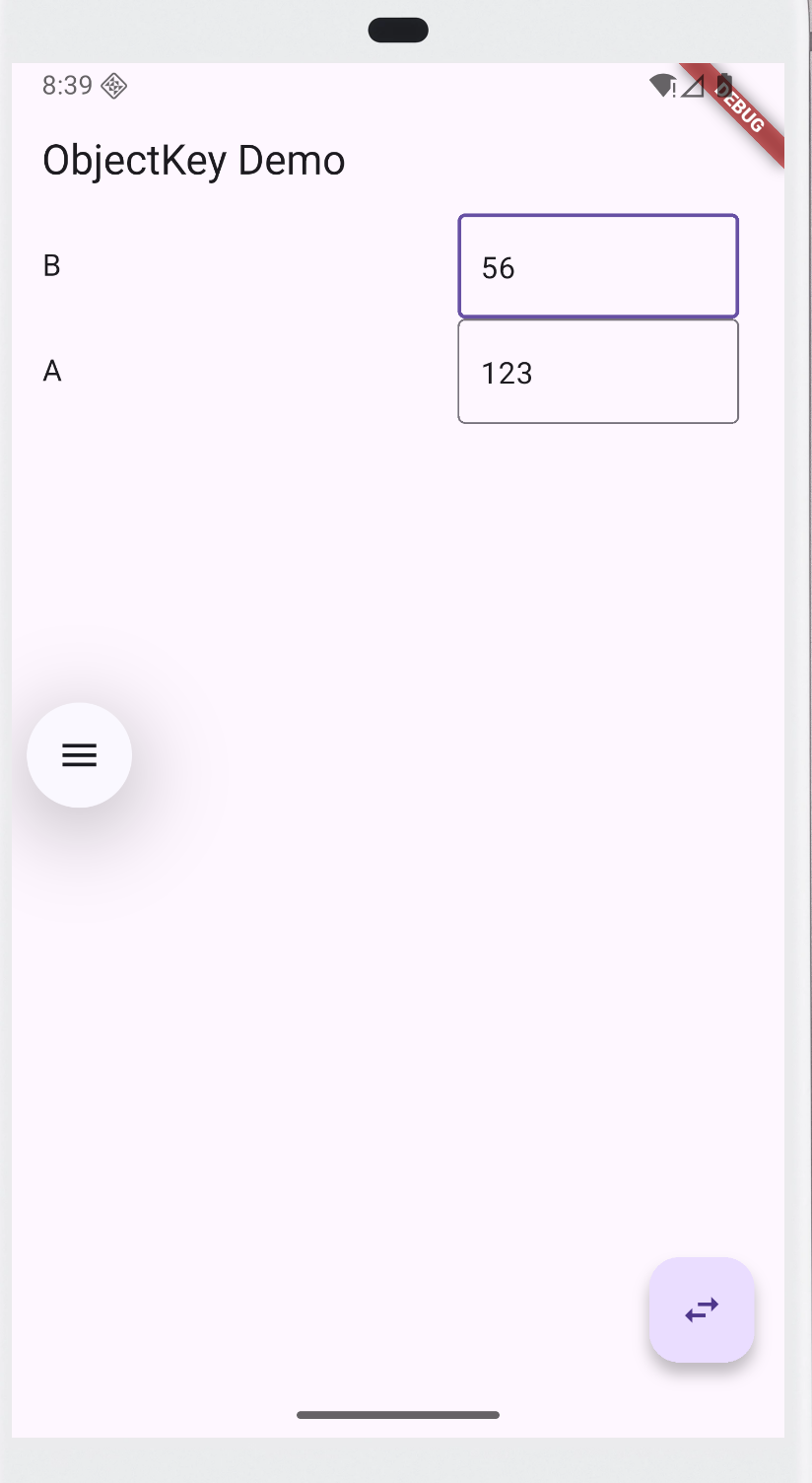
UniqueKey
每次创建都是全新的,永远不相等,不可以复用
import 'package:flutter/material.dart';
void main() => runApp(const MaterialApp(home: UniqueKeyDemo()));
class UniqueKeyDemo extends StatefulWidget {
const UniqueKeyDemo({super.key});
@override
State<UniqueKeyDemo> createState() => _UniqueKeyDemoState();
}
class _UniqueKeyDemoState extends State<UniqueKeyDemo> {
List<String> items = ["A", "B"];
void swap() {
setState(() {
items.insert(0, items.removeAt(1)); // 交换顺序
});
}
@override
Widget build(BuildContext context) {
return Scaffold(
appBar: AppBar(title: const Text("UniqueKey Demo")),
body: ListView(
children: items.map((e) {
return ListTile(
key: UniqueKey(), // ❌ 每次都是新的 key
title: Text(e),
trailing: SizedBox(
// ✅ 给 TextField 约束宽度
width: 150,
child: TextField(
decoration: const InputDecoration(
border: OutlineInputBorder(),
hintText: "输入点内容",
),
),
),
);
}).toList(),
),
floatingActionButton: FloatingActionButton(
onPressed: swap,
child: const Icon(Icons.swap_horiz),
),
);
}
}
每次交换顺序,输入框的内容都会丢失,因为 UniqueKey 让 Flutter 认为这是全新的 widget,旧的 state 全部销毁。

GlobalKey
访问State
全局唯一,可以在 widget 树外访问 State。
import 'package:flutter/material.dart';
void main() => runApp(const MaterialApp(home: GlobalKeyDemo()));
class GlobalKeyDemo extends StatefulWidget {
const GlobalKeyDemo({super.key});
@override
State<GlobalKeyDemo> createState() => _GlobalKeyDemoState();
}
class _GlobalKeyDemoState extends State<GlobalKeyDemo> {
final GlobalKey<_CounterState> counterKey = GlobalKey<_CounterState>();
@override
Widget build(BuildContext context) {
return Scaffold(
appBar: AppBar(title: const Text("GlobalKey Demo")),
// ✅ 使用 GlobalKey 包裹子组件
// key: counterKey : 指定 Counter 的 GlobalKey
// 在这里key: counterKey,flutter会帮我们把这个key传递给Counter组件
// state 会被正确地关联
body: Center(child: Counter(key: counterKey)),
floatingActionButton: FloatingActionButton(
onPressed: () {
// ✅ 直接通过 GlobalKey 访问子组件的 State
// counterKey.currentState : 获取 Counter 的 State
counterKey.currentState!.increment();
},
child: const Icon(Icons.add),
),
);
}
}
class Counter extends StatefulWidget {
const Counter({super.key});
@override
State<Counter> createState() => _CounterState();
}
class _CounterState extends State<Counter> {
int count = 0;
void increment() {
setState(() => count++);
}
@override
Widget build(BuildContext context) {
return Text("Count是: $count", style: const TextStyle(fontSize: 24));
}
}
运行后,点击右下角按钮,会直接修改子组件 Counter 的状态。这就是 GlobalKey 的强大之处:外部可以访问内部的 State。
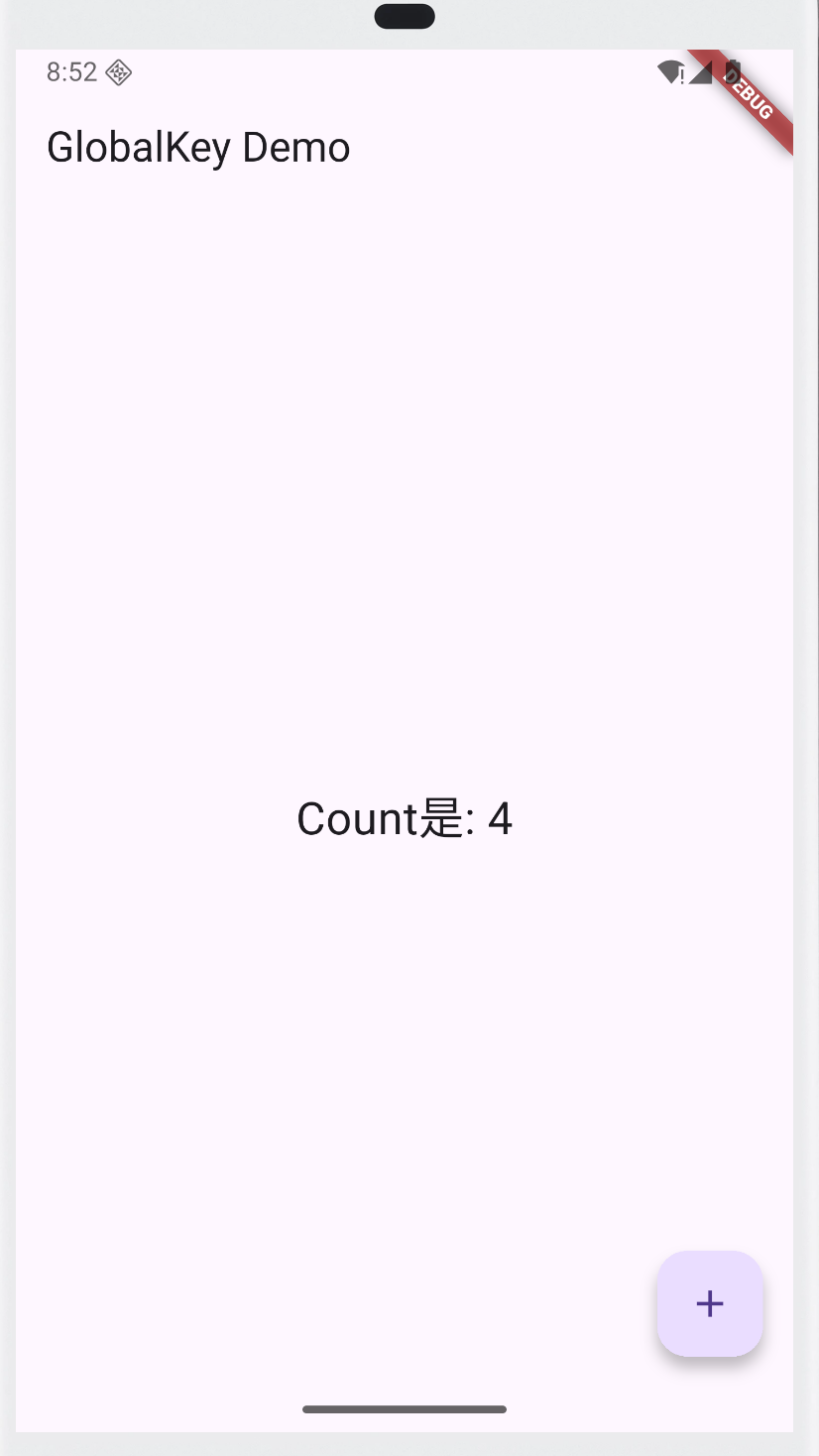
通过 GlobalKey获取FormState
final _formKey = GlobalKey<FormState>();
Form(
key: _formKey,
child: ...
);
// 使用
_formKey.currentState!.validate();
_formKey.currentState!.save();
final _formKey = GlobalKey<FormState>();
_formKey是一个GlobalKey<FormState>对象。- 它是一个标识符,类型参数
<FormState>限定了它只能绑定FormState实例。
Form(key: _formKey, child: ...)
- 当
Form被插入 widget 树时:- Flutter 调用
Form.createState(),创建一个新的FormState实例。 - 框架会把这个
FormState和_formKey关联起来。
- Flutter 调用
_formKey.currentState
- 返回与该 key 绑定的
FormState实例。这就是Formwidget 的状态对象。

