远程调用
OpenFeign 是⼀个声明式远程调⽤客户端;
RestTemplate 是⼀个编程式远程调⽤客户端;
OpenFeign 会自动进行负载均衡。
微服务间的调用
引⼊依赖
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.cloud</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-cloud-starter-openfeign</artifactId>
</dependency>
开启功能
@EnableFeignClients //启用Feign客户端
@EnableDiscoveryClient //开启服务发现功能
@SpringBootApplication
public class OrderMainApplication {
public static void main(String[] args) {
SpringApplication.run(OrderMainApplication.class, args);
}
}
@EnableFeignClients的作用
它的作用是让 Spring Boot 扫描并注册所有用 @FeignClient 注解的接口。其参数basePackages可以控制扫描哪些包中的 Feign 接口,比如:
@EnableFeignClients(basePackages = "org.example.order.feign")
表示只扫描 org.example.order.feign 包及其子包中的 @FeignClient 接口。
为什么“没写也可以”?: 这跟你 Spring Boot 启动类的位置 和 包结构有关。Spring Boot 启动类通常像这样:
@SpringBootApplication
public class OrderMainApplication {
public static void main(String[] args) {
SpringApplication.run(OrderMainApplication.class, args);
}
}
@SpringBootApplication 本身包含了 @ComponentScan,默认扫描启动类所在包及其子包。
只要你的 Feign 接口也在这些“子包”里,它自然就会被扫描到!
org.example.order
├── OrderMainApplication.java // 启动类
└── feign
└── StorageFeignClient.java // Feign 接口
在这种结构下,不写 basePackages 也可以,因为 feign 是启动类所在包的子包。
org.example.order
└── OrderMainApplication.java // 启动类
org.example.common.feign
└── StorageFeignClient.java // Feign 接口
这时候,如果你没写 @EnableFeignClients(basePackages = "org.example.common.feign"),这个 Feign 接口是不会被扫描到的。
声明客户端
// feign客户端:value = "service-product" 表示要调用的服务名称
@FeignClient(value = "service-product")
public interface ProductFeignClient {
//mvc注解的两套使用逻辑
//1、标注在Controller上,是接受这样的请求
//2、标注在FeignClient上,是发送这样的请求
@GetMapping("/product/{id}") // 发送Get请求
// @PathVariable("id")是Spring MVC的注解,用于从URL中提取变量值并将其绑定到方法参数上。
// 这里的"id"是URL中的变量名,@PathVariable("id")表示将URL中的"id"变量绑定到方法参数id上。
// 这样,当调用这个Feign客户端时,传入的id值会被自动映射到方法参数中。
Product getProductById(@PathVariable("id") Long id);
}
@PostMapping:发送Post请求
@DeleteMapping:发生delete请求
@PutMapping:发送Put请求
@FeignClient的基础参数
| 参数名 | 类型 | 默认值 | 说明 |
|---|---|---|---|
value/name |
String | - | 服务名称(必填),用于服务发现(如 Nacos/Eureka),与 url 互斥 |
url |
String | - | 直接指定服务地址(如 http://api.example.com),绕过服务发现 |
contextId |
String | - | 客户端 Bean 的唯一 ID,用于解决相同 value 的多客户端冲突 |
path |
String | "" |
所有请求的公共路径前缀(如 /api/v1) |
当使用 @FeignClient 注解时,Spring 会生成一个 Bean,其名称遵循以下规则:
- 如果指定了
value/name:@FeignClient(value = "service-product")→ Bean 名称为service-productFeignClient(自动追加FeignClient后缀) - 如果指定了
contextId:@FeignClient(contextId = "productApi")→ Bean 名称为productApi
使用
@Autowired
ProductFeignClient productFeignClient;
@Override
public Order createOrder(Long productId, Long userId) {
// 远程调用商品服务,获取商品信息
Product product = productFeignClient.getProductById(productId);
Order order = new Order();
order.setId(1L);
// 总金额
order.setTotalAmount(product.getPrice().multiply(new BigDecimal(product.getNum())));
order.setUserId(userId);
order.setNickName("zhangsan");
order.setAddress("beijing");
// 目前只有一个商品
order.setProductList(Arrays.asList(product));
return order;
}
第三方API调用
定义Feign 客户端接口
@FeignClient(value = "weather-client", url = "http://aliv18.data.moji.com")
public interface WeatherFeignClient {
@PostMapping("/whapi/json/alicityweather/condition")
String getWeather(@RequestHeader("Authorization") String auth,
@RequestParam("token") String token,
@RequestParam("cityId") String cityId);
}
value = "weather-client": 指定客户端名称(用于服务发现,若需负载均衡)。
url = "http://aliv18.data.moji.com": 直接指定目标服务的固定基础地址(向第三方接口发送请求,绕过服务发现)。
@PostMapping("/whapi/json/alicityweather/condition"):指定请求的 HTTP 方法(POST)和路径,拼接在 url 后形成完整请求地址:http://aliv18.data.moji.com/whapi/json/alicityweather/condition
| 注解 | 参数位置 | 示例请求结构 |
|---|---|---|
@RequestHeader |
请求头 | Authorization: APPCODE 93b7e1... |
@RequestParam |
URL 查询参数 | ?token=xxx&cityId=2182 |
使用Feign
@Autowired
WeatherFeignClient weatherFeignClient;
@GetMapping("/weather")
public String test01(){
String weather = weatherFeignClient.getWeather("APPCODE 93b7e19861a24c519a7548b17dc16d75",
"50b53ff8dd7d9fa320d3d3ca32cf8ed1",
"2182");
System.out.println("weather = " + weather);
return weather;
}
客户端负载均衡与服务端负载均衡区别
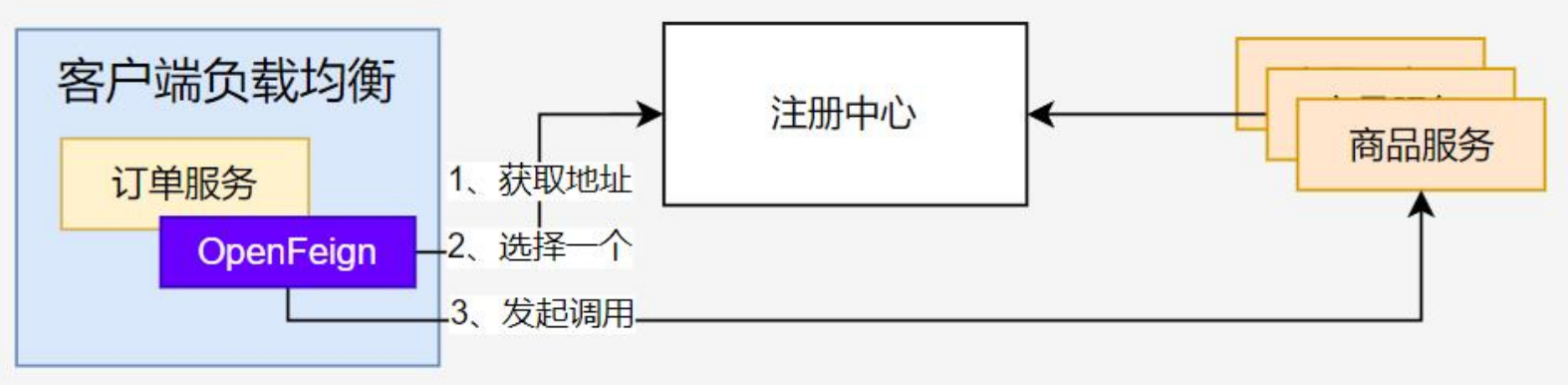
客户端负责均衡就是OpenFeign从注册中心获取相关服务的IP地址列表,然后根据负载均衡算法从里面选一个IP地址,最后发起调用。
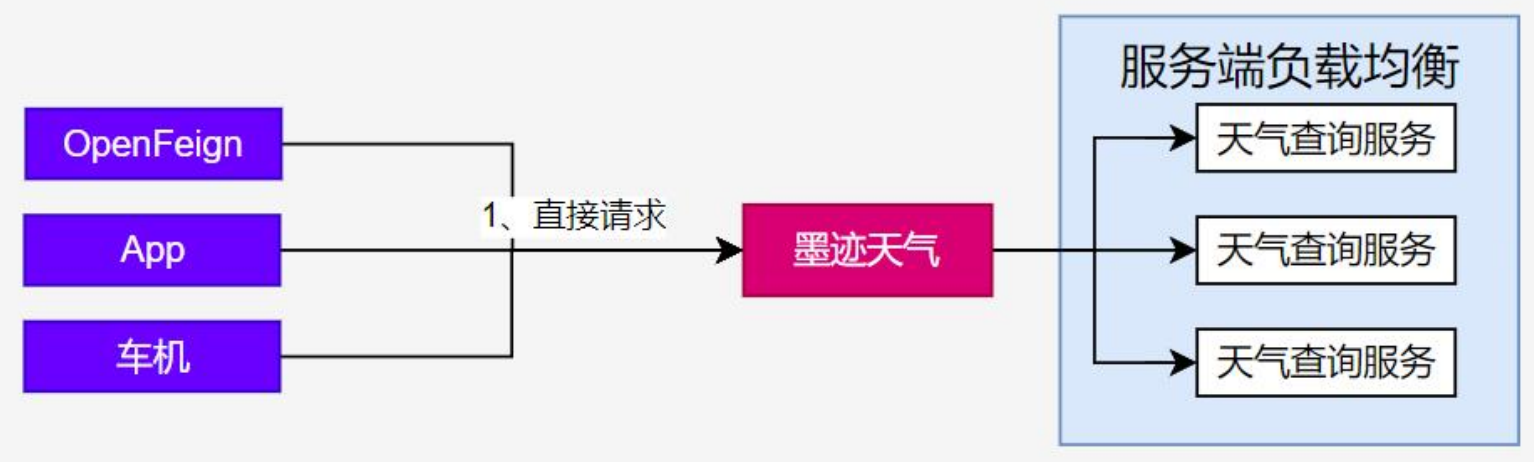
服务端负载均衡是,OpenFeign直接向墨迹天气发送请求,请求的发送方不负责负载均衡,有请求的接受方(墨迹天气)选择具体哪个服务器。
进阶配置
日志
在yaml文件里面配置日志级别
# 设置feign所在包下的日志级别为debug
logging:
level:
org.example.feign: debug
在配置类里面配置Bean
@Configuration
public class OrderConfig {
// Logger.Level.FULL 表示打印所有的请求和响应信息,包括头信息、正文和元数据
// Logger.Level.BASIC 表示只打印请求方法、URL、响应状态码和执行时间
// Logger.Level.NONE 表示不打印任何日志
// Logger.Level.HEADERS 表示打印请求和响应的头信息,但不打印正文
// Logger.Level.SIMPLE 表示只打印请求方法和URL,以及响应状态码和执行时间
// Logger.Level.DEFAULT 表示使用Spring Cloud默认的日志级别
// 得到的Logger.Level是一个枚举类型,表示Feign的日志级别。
@Bean
Logger.Level feignLoggerLevel() {
return Logger.Level.FULL;
}
}
超时控制
为什么需要超时控制
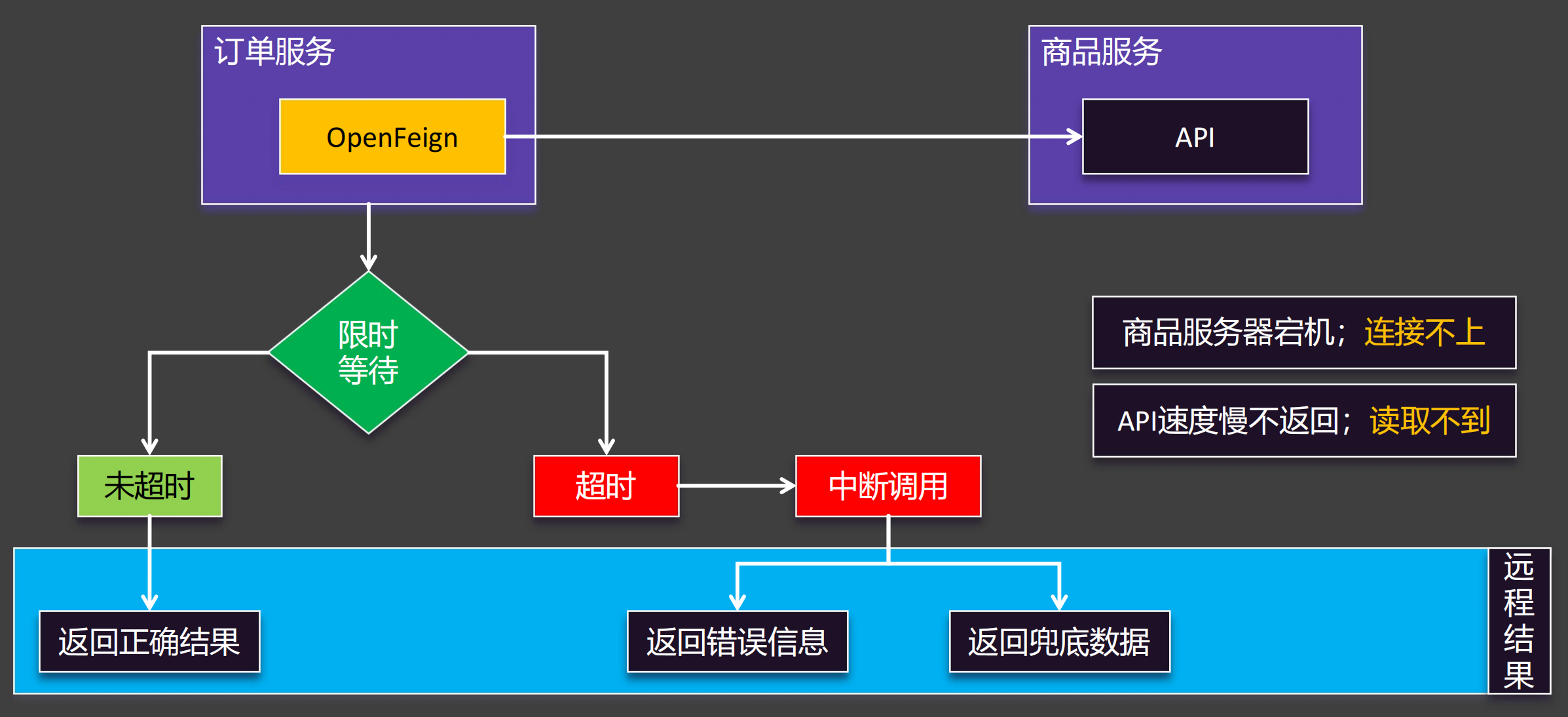
为什么需要超时控制? 如果没有超时控制,导致OpenFeign一直等待对方服务,会影响后面的调用,过多的请求挤压会导致服务雪崩。

一次远程调用的流程:首先是建立连接,连接建立之后再发送请求,接着B处理业务,B处理完业务之后再返回数据个A。
connectTimeout连接超时:是指第1步,建立连接的时间。OpenFeign默认超时是10秒。
readTimeout读取超时:是指A发送请求到B返回数据的时间,其中主要是B处理业务的时间。OpenFeign默认超时是60秒。
修改超时时间
在
application-feign.yml里面专门配置feignspring: cloud: openfeign: client: config: default: # 默认配置对所有Feign客户端生效 logger-level: full # 日志级别为full connect-timeout: 1000 # 连接超时时间为1000毫秒 read-timeout: 2000 # 读取超时时间为2000毫秒 service-product: # 针对service-product的Feign客户端配置 logger-level: full # 日志级别为full connect-timeout: 3000 # 连接超时时间为3000毫秒 read-timeout: 5000 # 读取超时时间为5000毫秒在
application.yml里面引入feign的配置spring: application: name: service-order profiles: include: feign # 引入feign配置文件(application-feign.yml) cloud: nacos: server-addr: 127.0.0.1:8848 config: group: order
重试机制
远程调用超时失败后,还可以进行多次尝试,如果某次成功返回ok,如果多次依然失败则结束调用,返回错误
OpenFeign默认使用的是Retryer.NEVER_RETRY的模式,也就是不会重试。
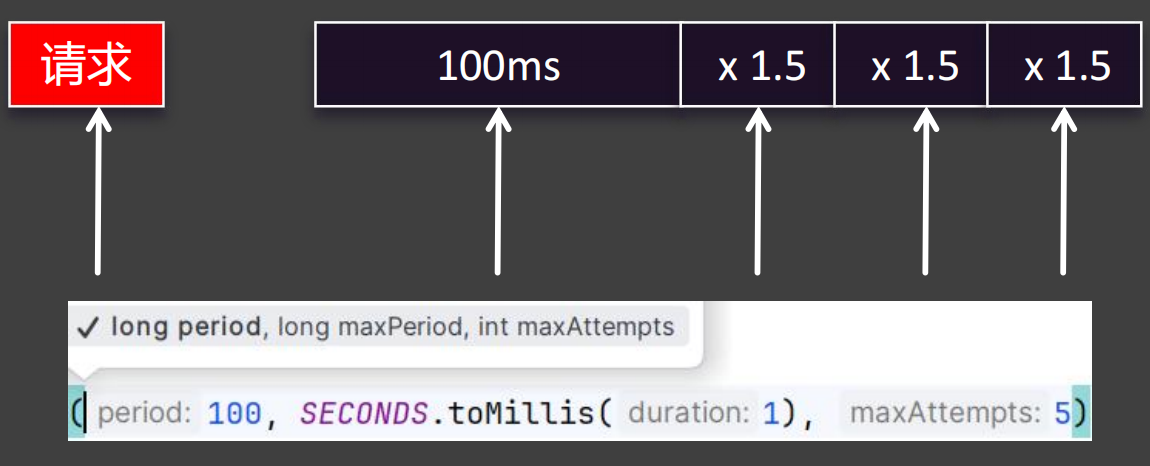
我们可以自己设置充实机制,如上图:
period是间隔时间,100毫秒maxPeriod:最大间隔时间,是1秒maxAttempts:最大尝试次数,5次- 上面配置的意思就是:一个请求发送失败后,会继续尝试发送。第一次是
100毫秒之后,第二次是100*1.5毫秒之后,第三次是100*1.5*1.5毫秒之后。但是最大间隔是1秒钟。会这样尝试5次。
使用yaml配置
这个方法只能使用默认重试器
spring:
cloud:
openfeign:
client:
config:
default:
logger-level: full
connect-timeout: 1000
read-timeout: 2000
service-product:
logger-level: full
connect-timeout: 3000
read-timeout: 5000
retryer: feign.retryer.Default # 使用默认的重试器
feign.retryer.Default使用的是默认的重试器:this(100L, TimeUnit.SECONDS.toMillis(1L), 5);
public static class Default implements Retryer {
private final int maxAttempts;
private final long period;
private final long maxPeriod;
int attempt;
long sleptForMillis;
public Default() {
this(100L, TimeUnit.SECONDS.toMillis(1L), 5);
}
public Default(long period, long maxPeriod, int maxAttempts) {
this.period = period;
this.maxPeriod = maxPeriod;
this.maxAttempts = maxAttempts;
this.attempt = 1;
}
}
自定义重试器(推荐)
@Configuration
public class FeignConfig {
@Bean
public Retryer feignRetryer() {
// 最大重试次数为3,初始间隔100ms,最大间隔1s
return new Retryer.Default(100, 1000, 3);
}
}
注意,yaml里面不能配置retryer。
如果想使用默认的重试器:
@Configuration
public class FeignConfig {
@Bean
public Retryer feignRetryer() {
// 使用默认重试器
return new Retryer.Default();
}
}
拦截器
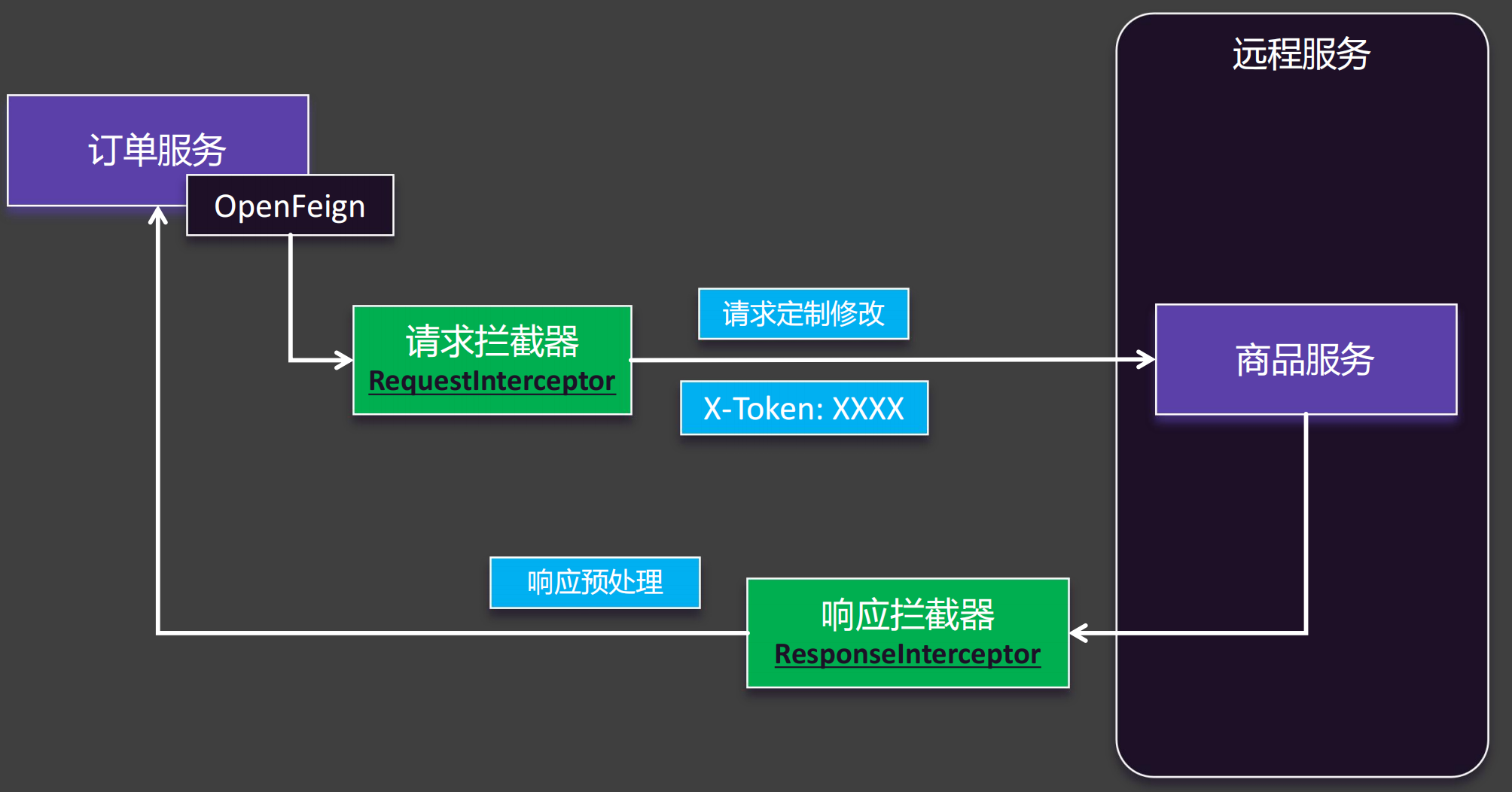
OpenFeign在发送请求之前,会经过一个请求拦截器,用于对请求做一些修改,再发给远程服务。
远程服务将数据返回给订单服务之前,会经过响应拦截器,做一些响应预处理,之后才把数据返回给订单服务。
请求拦截器使用的频率多一些,比如:我们把X-Token统一放入请求头中。
创建拦截器:
@Component
public class XTokenRequestInterceptor implements RequestInterceptor {
/**
* 请求拦截器
* @param template 请求模板, 可以在这里修改请求头、请求参数等
*/
@Override
public void apply(RequestTemplate template) {
System.out.println("XTokenRequestInterceptor ....... ");
template.header("X-Token", UUID.randomUUID().toString());
}
}
在 Spring Cloud OpenFeign 中,实现 RequestInterceptor 接口并注册为 Spring Bean 后,该拦截器会自动生效,因为 Spring Cloud Feign 自动收集所有 Spring 容器中的 RequestInterceptor Bean 并应用
使用HttpServletRequest获取Token:
@GetMapping("/product/{id}")
public Product getProduct(@PathVariable("id") Long productId,
HttpServletRequest request){
String header = request.getHeader("X-Token");
System.out.println("hello .... token=【"+header+"】");
Product product = productService.getProductById(productId);
return product;
}
Fallback机制
Fallback:兜底返回
注意:此功能需要整合 Sentinel 才能实现
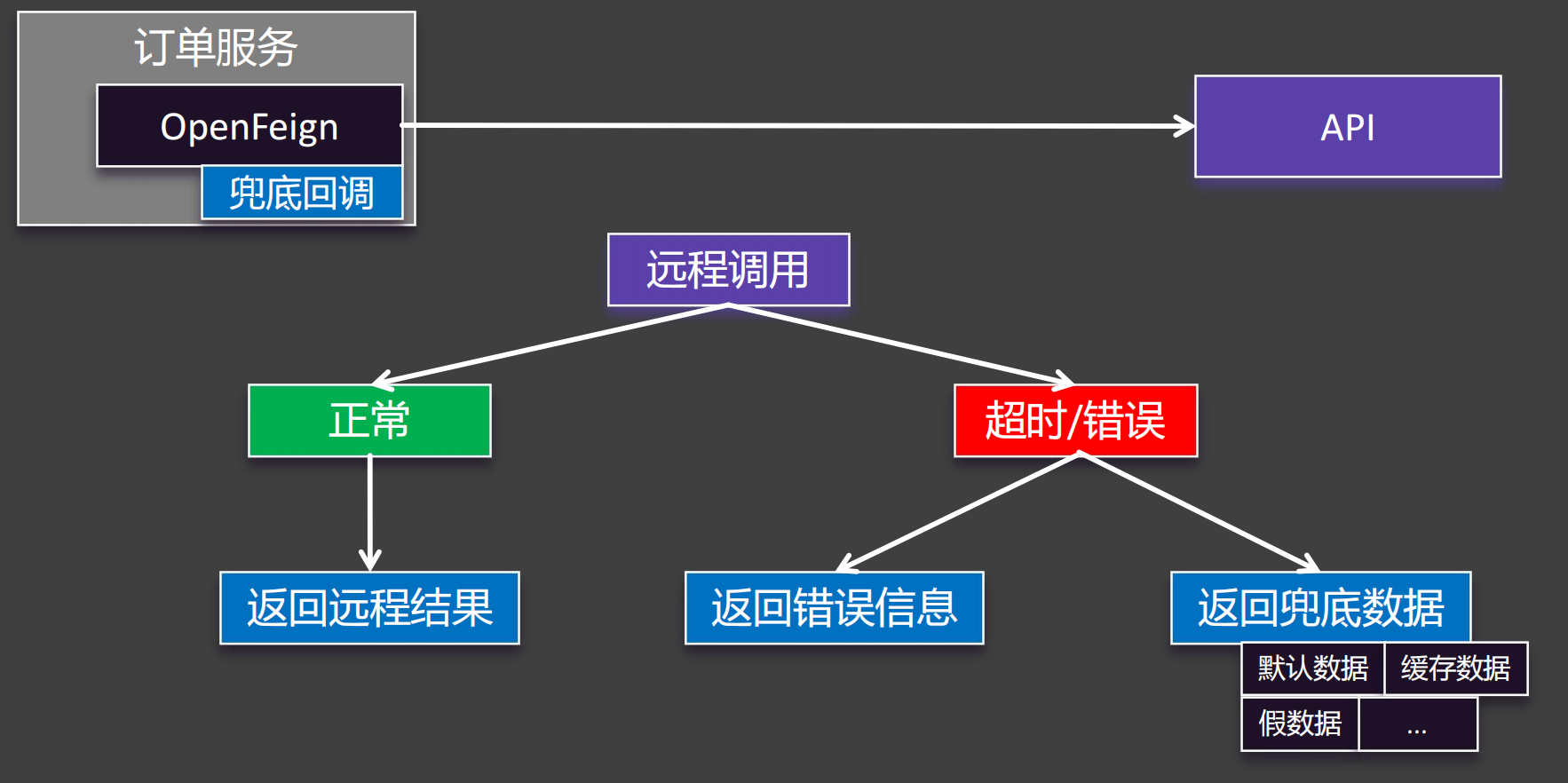
在超时控制的章节中,我们谈到如果超时,我们就结束请求,并返回错误信息。但是,有时候我们不希望这个业务逻辑结束,希望这个业务可以继续往后面走。比如查询库存,如果超时,我们希望可以返回库存为0,这样我们仍然可以进行后面的业务逻辑。这个时候,我们就需要兜底数据(兜底回调)。
创建兜底Bean
需要实现相关的FeignClient的接口
@Component
public class ProductFeignClientFallback implements ProductFeignClient {
@Override
public Product getProductById(Long id) {
System.out.println("兜底回调....");
Product product = new Product();
product.setId(id);
product.setPrice(new BigDecimal("0"));
product.setProductName("未知商品");
product.setNum(0);
return product;
}
}
指定fallback
@FeignClient(value = "service-product" ,
configuration = ProductFeignConfig.class,
fallback = ProductFeignClientFallback.class)
public interface ProductFeignClient {
@GetMapping("/product/{id}")
Product getProductById(@PathVariable("id") Long id);
}
引入Sentinel依赖
<!-- sentinel 熔断降级 -->
<dependency>
<groupId>com.alibaba.cloud</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-cloud-starter-alibaba-sentinel</artifactId>
</dependency>
添加配置
在application-feign.yml里面
feign:
sentinel:
enabled: true
不同Feign客户端使用不同的重试器和拦截器
重试器
设置通用的Retryer,对所有该微服务下的OpenFeignClinet起作用
// 通用重试器(默认)
@Bean
@Primary // @Primary 注解表示这个 Bean 是首选的,如果有其他同类型的 Bean,会优先使用这个 Bean
public Retryer defaultFeignRetryer() {
return new Retryer.Default(10, 1000, 5);
}
@Primary 注解的作用是当 Spring 容器中存在多个相同类型的 Bean 时,优先选择标注了 @Primary 的 Bean 进行注入。它主要用于解决 Bean 冲突的问题。
设置特定的Retryer:
// 特定服务配置
//@Configuration // 这里不需要使用@Configuration 注解,因为这个配置类是为 Feign 客户端提供的配置
public class ProductFeignConfig {
@Bean
public Retryer productRetryer() {
return new Retryer.Default(10, 1000, 2);
}
}
如果加了
@Configuration会报如下错误:Parameter 0 of method feignBuilder in org.springframework.cloud.openfeign.FeignClientsConfiguration$DefaultFeignBuilderConfiguration required a single bean, but 2 were found: - defaultFeignRetryer: defined by method 'defaultFeignRetryer' in class path resource [org/example/config/OrderConfig.class] - productRetryer: defined by method 'productRetryer' in class path resource [org/example/config/ProductFeignConfig.class]说明 Feign 在构建 FeignClient 时,需要注入一个
RetryerBean,但此时 Spring 容器中出现了两个符合条件的 Bean,Spring 不知道用哪个。这个问题产生的真正原因是:
你把
OrderConfig和ProductFeignConfig都作为常规的@Configuration放进了 Spring 主上下文中,而不是只作为 Feign 专用的配置类使用。 这会导致 两个 Retryer Bean 都被注册到全局容器中,从而导致冲突。
在ProductFeignClient单独指定配置:
@FeignClient(value = "service-product" ,configuration = ProductFeignConfig.class)
public interface ProductFeignClient {
@GetMapping("/product/{id}")
Product getProductById(@PathVariable("id") Long id);
}
configuration = ProductFeignConfig.class : 会自动加载你指定的配置类,并注入其中的 @Bean,即使它没有被标注为 @Component 或 @Configuration。
Spring Cloud OpenFeign 的
@FeignClient注解会在启动时扫描并加载你通过configuration属性指定的配置类,即使没有在ProductFeignConfig上面标注@Configuration。Spring 会把它作为 FeignClient 的局部配置类加载进一个“局部 ApplicationContext”,只对这个 FeignClient 生效。
configuration 的作用是: 为某个 FeignClient 单独指定 Spring 配置类(用于替代默认配置),配置内容包括:Retryer、Logger.Level、Decoder、Encoder、RequestInterceptor 等。
| 配置项类型 | 用途 |
|---|---|
Retryer |
自定义重试策略 |
Logger.Level |
日志级别(如 NONE、BASIC、FULL) |
RequestInterceptor |
给请求加 Header、Token 等 |
Decoder / Encoder |
自定义请求解码器/编码器(如支持自定义格式) |
Contract |
指定注解解析方式(如 SpringMVC 默认) |
ErrorDecoder |
自定义错误解码器(比如统一处理异常) |
拦截器
定义单独的拦截器
// @Component 这里不需要
public class XTokenProductRequestInterceptor implements RequestInterceptor {
/**
* 请求拦截器
* @param template 请求模板, 可以在这里修改请求头、请求参数等
*/
@Override
public void apply(RequestTemplate template) {
System.out.println("XTokenRequestInterceptor ....... ");
template.header("X-Token", UUID.randomUUID()+ "-product");
}
}
放到配置类中
// 特定服务配置
//@Configuration // 这里不需要使用@Configuration 注解,因为这个配置类是为 Feign 客户端提供的配置
public class ProductFeignConfig {
@Bean
public Retryer productRetryer() {
return new Retryer.Default(10, 1000, 2);
}
@Bean
public RequestInterceptor xTokenProductRequestInterceptor() {
return new XTokenProductRequestInterceptor();
}
}
FeignClient指定
@FeignClient(value = "service-product" ,
configuration = ProductFeignConfig.class, // 指定ProductFeignConfig 这个配置
fallback = ProductFeignClientFallback.class)
public interface ProductFeignClient {
@GetMapping("/product/{id}")
Product getProductById(@PathVariable("id") Long id);
}

